Consulting firm McKinsey has projected that the Internet of Things (IoT) could enable global value between $5.5 trillion – $12.6 trillion by 2030. This estimation encompasses the value derived by consumers using IoT products and services. However, it is predicted that around 65% of this value will come from business-to-business (B2B) applications. And within the B2B sector, the primary drivers of value projected are operation optimisation (41%) and condition-based maintenance (12%).
2030 is still some time away, but how close are we to realising this value?
The IoT has already connected over 14 billion devices worldwide, but being a relatively new technology, it faces its share of challenges and obstacles. According to a recent survey on IoT deployments, only 42% of companies considered their projects successful. However, it’s important to consider that 50% of those surveyed were in the trial or pilot phase, which provides valuable insights into identifying barriers to success. Encouragingly, when compared to the 2020 survey results, the 2023 survey indicates a notable 28% increase in success rates. Additionally, research from ABI reveals that satellite IoT projects have a comparable but increased success rate, with approximately 50% of participants considering their projects successful.
As the adoption and success of IoT continues to accelerate, demonstrating a positive return on investment (ROI) becomes increasingly essential. Here at Ground Control, we are privileged to work on a wide range of IoT deployments every day. Our projects span various industries, from operators seeking to minimise downtime in the Oil and Gas sector, to those in Utilities handling mission-critical data, and even those facilitating telehealth via medical drone deliveries and remote nurse tracking. Drawing on these experiences, we’ve created this article to highlight the challenges we most commonly see and potential solutions to guide you on the path to success. But first…
How to define IoT project success
Defining IoT project success involves aligning project goals with overall objectives, setting specific and measurable KPIs, and quantifying expected benefits and ROI. Establishing baselines and targets, tracking progress, and analysing data against the defined metrics are crucial. In our experience, customers often focus on immediate challenges and short-term gains and this can lead to issues regarding scalability and the ability to adapt to future needs further down the line. When embarking on an IoT installation, regular iteration and improvement can mark the difference between success or not. In short, for many IoT projects success is dependent on companies being proactive.
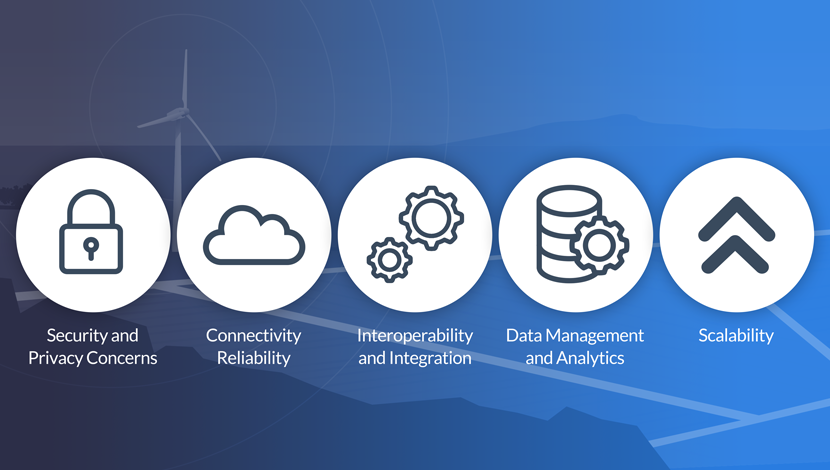
5 common IoT deployment challenges and potential solutions to overcome them

1. Challenge: Security and privacy concerns
Within the vast IoT ecosystem, the extensive network of interconnected devices creates numerous potential entry points for cyberattacks. Each connected device becomes a potential vulnerability that malicious actors can exploit. The sheer volume of data generated and transmitted by IoT devices raises significant concerns about privacy. Safeguarding personal information and ensuring data protection become of paramount importance in this interconnected landscape.
From a technical perspective, security emerges as the foremost obstacle in IoT deployments. As IoT solutions continue to evolve, security measures must also advance. It is an ongoing and dynamic process that requires continuous improvement and this inherent characteristic poses significant challenges.
These concerns are further emphasised by notable cyberattacks that have made headlines. In 2021, a cyberattack on Colonial Pipeline forced a temporary shutdown of 5,500 miles of pipeline, impacting critical infrastructure. In another instance, an attempt was made to tamper with the levels of sodium hydroxide in Oldsmar, Florida’s water supply. Additionally, the ‘AcidRain‘ malware attack in 2022 caused severe and prolonged disruptions on a mass scale. This attack targeted and disabled Viasat’s KA-SAT broadband service’s satellite modems, affecting thousands of users in Ukraine and across Europe.
Potential solutions: Secure network design and data encryption
Addressing the security concerns in IoT deployments requires a multi-layered approach to IoT security. Implementing secure network architectures, employing data encryption, practicing best access control practices, and leveraging private network solutions, all strengthen organizations overall security posture in IoT deployments.
Secure Network Architecture: A robust and secure network architecture is crucial in addressing IoT security concerns. Companies should design their networks with measures such as network segmentation, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. By dividing the network into segments and implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems, the impact of potential breaches can be contained, and real-time threat identification and mitigation can be achieved.
Data Encryption: Protecting IoT data through encryption is paramount. Strong encryption algorithms and secure key management practices should be employed to ensure the confidentiality of sensitive information. By encrypting data at rest and in transit, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their IoT deployments.
Best Practice Access Control: Implementing best practices for access control and identity management is a simple yet effective way to strengthen IoT security. Regularly reviewing access privileges, promptly revoking access for former employees or compromised accounts, and monitoring for suspicious activities all contribute to an enhanced security posture, mitigating potential risks.
Private and Secure Networks: Depending on the nature of the data handled by an IoT application, a completely secure and private network may be necessary. Solutions like SCADASat provide secure, private networks for handling sensitive data, ensuring end-to-end security and protecting against unauthorized access.
2. Challenge: Connectivity reliability
The success of IoT relies heavily on reliable connectivity. Without a consistent means of transmitting data, the value of IoT is diminished. Obtaining a comprehensive view of operations is crucial for making informed business decisions. Fragmented data can lead to inaccurate insights, resulting in suboptimal business decisions.
Currently, only 25% of the world’s landmass is covered by cell towers. While 5G deployment is underway and will be able to support a much larger volume of devices, the shorter wavelengths mean 5G has a much shorter range than its predecessor. For some deployments, cellular coverage will be sufficient. But for those with assets in remote locations whereby cellular may be intermittent or unavailable, challenges arise; and a staggering 75% of businesses reported struggling with connectivity issues when trialling IoT projects.

Potential solutions: diversify connectivity portfolio, implement redundant network architectures and regular maintenance
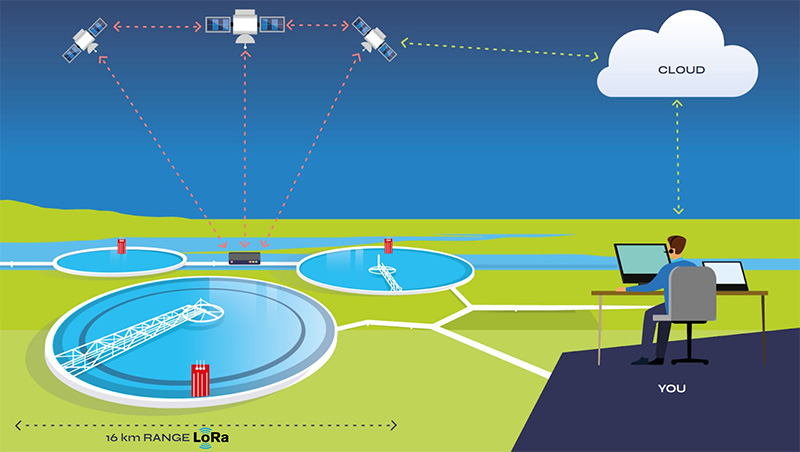
Diversifying your connectivity portfolio involves adopting multiple connectivity technologies, including cellular, satellite, and LPWAN, to create a more resilient network infrastructure. By leveraging diverse connectivity options, organisations can minimise the impact of network outages, ensure continuous data transmission and balance costs. Just one example and one we’re increasingly seeing is satellite alongside LoRaWAN. Typically, sensors connected via LoRaWAN transmit data to a hub; the hub then optimises the data payload to reduce transmission costs, and from there transmits the data packet via cellular where and when available, and satellite when LTE is unavailable.
Implementing redundant network architectures is another effective strategy. This entails establishing backup systems and redundant connections to provide alternate pathways for data transmission. Redundancy mitigates the risk of single points of failure and enhances the reliability of the IoT network, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity even during network disruptions. One of our largest clients actually have satellite implemented as their third failover (cellular first, fibre second). Their satellite setup hasn’t failed once in 27 years and is the system they consider the most reliable.
What’s more, regular maintenance is vital for sustaining reliable connectivity. Conducting regular inspections, monitoring network performance, and performing necessary updates and maintenance tasks help identify and resolve potential issues proactively.
3. Challenge: Interoperability and integration
IoT projects encounter hurdles in achieving interoperability and integration across devices and systems. Inconsistent protocols, standards, and proprietary technologies create barriers to seamless data exchange and collaboration. These challenges result in data fragmentation, scalability limitations, and increased complexity in managing integrated IoT environments.
Potential solutions: APIs, middleware and gateway devices
Despite some really promising and exciting developments, it’s likely that widespread, tried and tested, and truly seamless interoperability – including device and connectivity – is a few years away. So many companies will still need to either utilize multiple SIM cards, and/or devices to make their network work for their IoT deployment. But open standards and protocols play a crucial role in addressing interoperability and integration challenges. By adopting open standards, organizations can ensure compatibility and seamless communication between different IoT devices and systems.
Additionally implementing robust APIs facilitates smooth integration and interoperation, enabling data exchange and interoperability across diverse components. Moreover, leveraging middleware solutions and gateway devices helps bridge the gap between incompatible technologies, enhancing interoperability and integration capabilities.
4. Challenge: Data management and analytics
Data management and analytics pose critical challenges in IoT projects. The sheer volume and diversity of data generated by connected devices make it daunting to collect, store, process, and derive meaningful insights. Organisations struggle to handle the velocity and real-time processing requirements of IoT data. Ensuring data quality, integrity, and security across heterogeneous data sources is another significant challenge. Furthermore, scalability issues arise as the number of devices and data sources increases.
Potential Solutions: Data management platforms, analytics tools and machine learning algorithms
Organisations can address data management and analytics challenges in IoT projects by adopting comprehensive data management platforms. These platforms facilitate efficient data collection, integration, and storage from diverse sources, ensuring data quality and reliability. Advanced analytics tools empower organisations to process and analyse IoT data efficiently and effectively, extracting valuable insights for informed decision-making.
What’s more, machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics can be used to identify patterns and drive actionable intelligence. When used appropriately, these can ensure companies can drive true value from their data and thus IoT deployment.

5. Challenge: Scalability
When scaling an IoT project, various challenges become more pronounced. The costs associated with scaling can be significant, including expenses for hardware, connectivity, data storage, and maintenance. Managing and maintaining the project also becomes more complex and expensive as the number of devices and systems increases.
Battery life and power consumption pose significant challenges in scaled IoT projects. With more devices consuming more power, effectively managing power consumption and extending battery lives becomes crucial.
Scaling also intensifies challenges in data interoperability, security, and management. Ensuring interoperability and compatibility between devices and systems becomes more complex as numbers increase. Robust security measures must be implemented to protect against the growing risks of security breaches. Additionally, managing and processing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices becomes a significant challenge that requires suitable infrastructure and tools.
Potential Solutions: Prioritise scalable architecture, carefully consider device choices and leverage edge computing
Often scale is where in-house server infrastructure falls short for IoT applications. Cloud infrastructure for IoT applications encompasses not only traditional data processing and storage services but also gateway services that facilitate data collection and device interaction. These include HTTP/MQTT servers and WebSocket servers. Scalability is a crucial factor when designing cloud infrastructure for IoT. As your device count increases, your cloud infrastructure must seamlessly scale alongside it. IoT cloud platforms offer superior scalability compared to physical servers maintained in-house. Leading cloud service providers including AWS, Azure, GCP, or Macrometa can all provide robust and scalable solutions.
Implementing edge computing can also alleviate the burden on centralised cloud infrastructure and enhance scalability. By performing data processing and analysis at the edge of the network, closer to the IoT devices, you can reduce latency, minimise bandwidth requirements, and improve overall system performance.
Additionally, it’s important to evaluate network providers that can support your scaling requirements and ensure seamless connectivity across your IoT ecosystem. We’d recommend considering solutions such as low power, wide area networks (LPWAN) or satellite as both offer extended range and scalability.
To address challenges of increased power consumption, companies can explore energy-efficient IoT devices, implement power-saving features such as sleep modes, and utilise power management techniques to prolong battery life. Moreover, alternative power sources, such as solar or kinetic energy, can prove key for long-term sustainability.
Security should always be a top priority, but as mentioned, when scaling this is even more crucial. Companies can strengthen security by adopting a multi-layered approach. Incorporate encryption techniques, secure authentication protocols, and regular security audits. Implement secure coding practices and provide ongoing training to your team to enhance security awareness and ensure compliance with industry best practices.
The above list is by no means exhaustive, but we hope it highlights the importance of staying proactive. By acknowledging the evolving nature of IoT, the improving success rates, and the valuable insights gained during pilot phases, organisations can overcome hurdles and capitalise on the immense potential offered by IoT deployments.
Want some advice on your IoT project?
As a trusted partner for IoT projects worldwide, we have helped businesses across diverse industries achieve their goals. Complete the form below to start your journey with us.