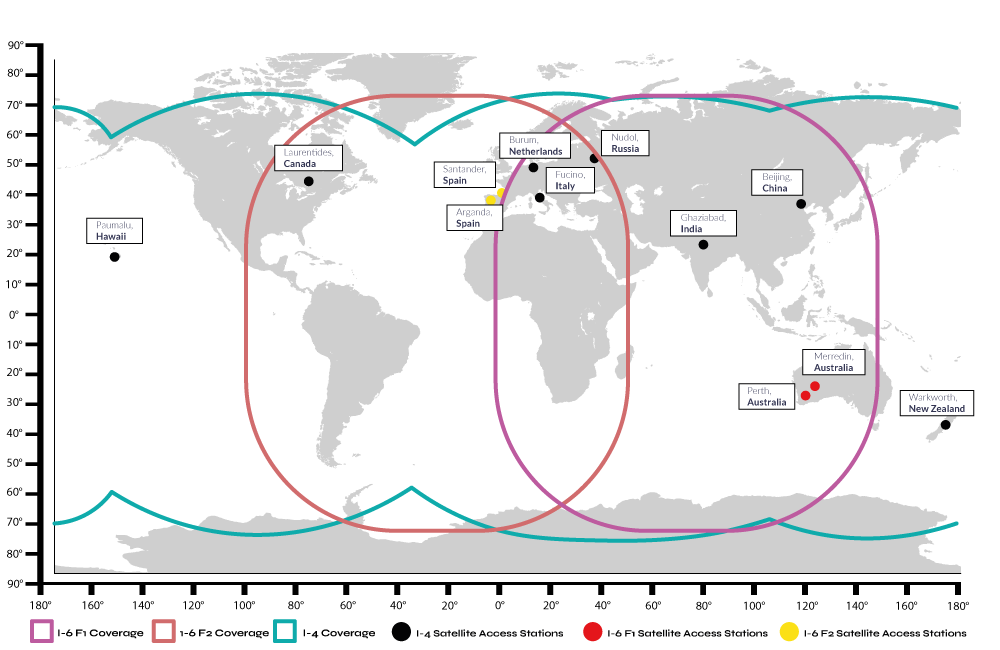
Satellite Names and Orbital Locations
- I-4 Americas 98° West
- Alphasat EMEA (Europe, Middle-East, Africa) 24.8° East
- I-4 Asia-Pacific 143.5° East
- I-4 MEAS – 64° East
The Next Generation of Inmarsat/Viasat Satellites
The Inmarsat I-6 F1 launched on 22nd December 2021, followed by the I-6 F2 in 2023. Both are dual-band satellites and support both L-Band and Ka-Band frequencies. With the launch, Inmarsat/Viasat now supports four times the amount of traffic than previously, which means faster speeds and continued reliability of service. The new satellites also deliver greater coverage.
Satellite Access Stations and the Primary NOC
Inmarsat/Viasat has 32 Satellite Access Stations (SAS) at strategic locations through the world that are all privately interconnected. The 6 primary SAS stations are located in New York, Hawaii, Hong Kong, Italy and Amsterdam. The Primary Network Operations Center (NOC) is located in London UK, and performs the coordination of all network activities, monitoring and troubleshooting.
Excellent in Stormy Weather
BGAN, BGAN M2M and IDP terminals all use the L-band for reception and transmission (the L-band has a very long wavelength); this is able to penetrate through clouds and other atmospheric conditions far better than large satellite dishes.
Can BGAN, BGAN M2M, or IDP be Used for Mobile Applications?
Depending on the antenna, yes. An auto-pointing antenna will relocate the satellite when the asset moves. Inmarsat/Viasat are in the process of building an omni-directional antenna which will make this process even faster and more reliable. If you are looking for a BGAN terminal with an auto-pointing antenna, we recommend the MCD-4800. The Cobham Explorer 323 is another great option that works on both BGAN and BGAN M2M airtime. For IDP we would recommend the ST6100.
What are the Differences Between the Wide, Regional and Narrow Beams?
Beams are what the Inmarsat/Viasat satellites transmit onto Earth and there are three beams they use… Wide beams for pointing signal strength, Regional beams for Voice and SMS, and Narrow beams for Internet.
Wide beam (not registered): This is the beam that you use for pointing. Minimum signal should be 50 or higher as seen on your Web Interface of the BGAN terminal.
Regional beam (registered): From the Web Interface of any BGAN terminal clicking on the “Register” button allows the terminal to make and receive phone calls and SMS messages. It is not for actively passing data (Internet) traffic… For that option to occur, click on “Start Data Session” from the Web Interface. Typical signal when in a Regional Beam is high 50s (usually 57-59).
Narrow beam (registered): These are the data/Internet beams (shown in a graphic below) and are used when clicking on “Start Data Session” from the Web Interface of any BGAN terminal. This establishes an active PDP context and IP data is allowed to pass from a connected device to the Internet. An ideal signal should be 65 or higher once establishing a connection with a BGAN Narrow Beam. Please note that a data connection may fall back to the regional beam after about 2.4 minutes of data inactivity.
If your narrow beam signal is bouncing between 60 and 63, it could be a pointing issue or the antenna/mount may be loose and moving or not pointed correctly. Please to take time to find the highest signal strength possible with your terminal for best results..
Interesting Facts On Inmarsat/Viasat Satellites and Coverage Area
Each Inmarsat/Viasat satellite can generate 19 wide beams and more than 200 narrow spot beams. These can quickly be reconfigured and focused anywhere on Earth to provide extra capacity where needed. Information on Inmarsat/Viasat Wide Beams and Narrow “Spot” Beams.
Some of the spacecraft’s impressive features include:
- The I-4 body – approaching the size of a double-decker bus at 7m x 2.9m x 2.3m
- Solar arrays – approaching the width of a football pitch, with an immense wing span of 45 meters
- Solar panels – combining conventional silicon with advanced gallium arsenide (GaAs) cells for optimum efficiency
- Digital signal processor – controlling the antennas, beam forming and channel allocation
- Reflector – 9 meters wide and designed to unfurl in orbit like a giant flower
- Antennas – 120 helix elements combined in a single flexible array
- Thrusters – both chemical and plasma ion for orbital station keeping
Look Angle Map
If you know your location on the map below, you can approximate the compass heading, as well as how many degrees up from the horizon one of the Inmarsat/Viasat satellites will be.
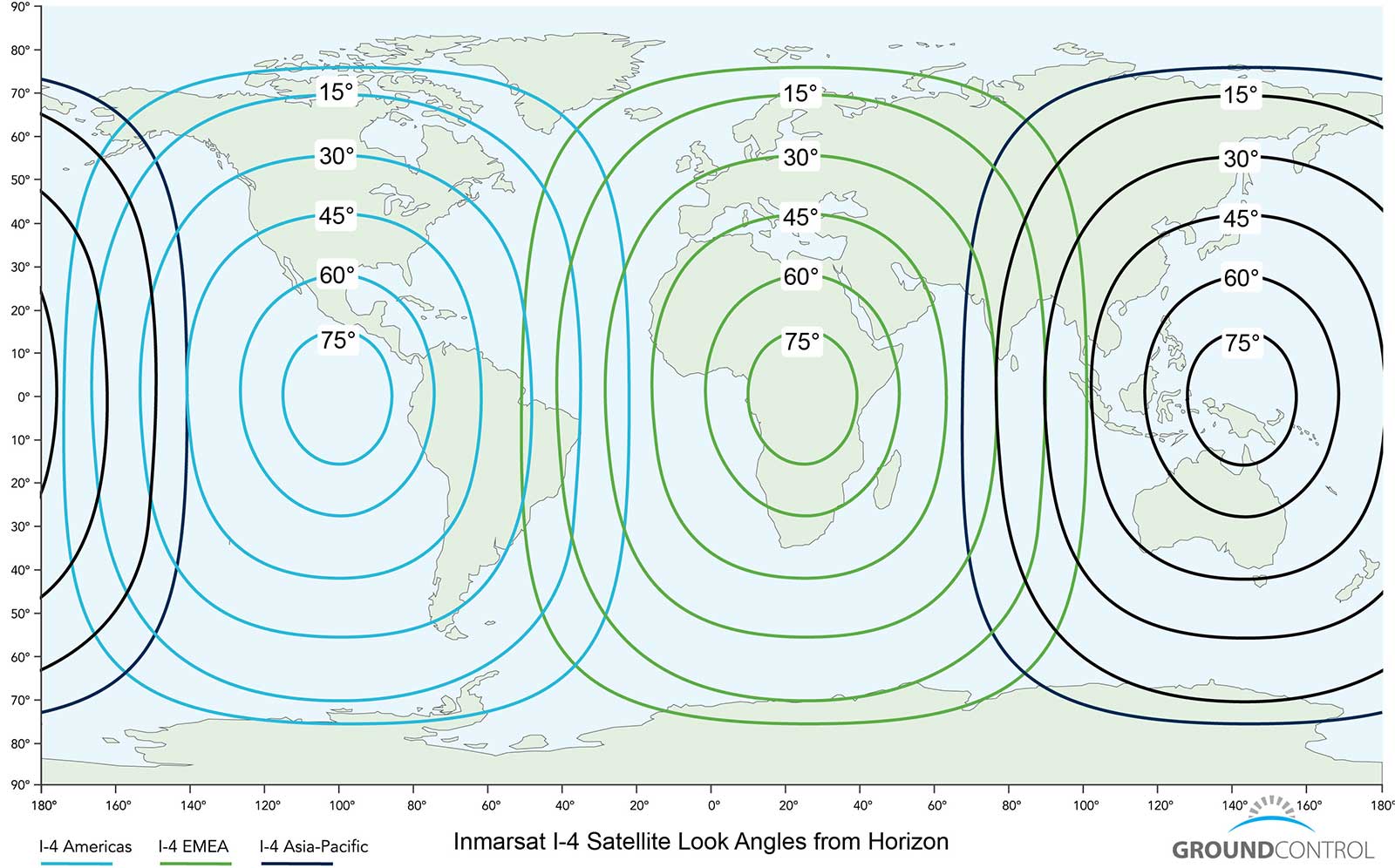
The circular lines on the map show the “Look Angle” of the nearest Inmarsat/Viasat BGAN satellite to help you locate a satellite. For example, to connect from California, a BGAN terminal will need to point south-south-east and tilt the BGAN terminal face up 45° degrees from a level horizon, while a BGAN terminal in Nigeria will aim east-south-east and 60° degrees up. Some BGANs come with a small compass built into the terminal to help point a terminal.
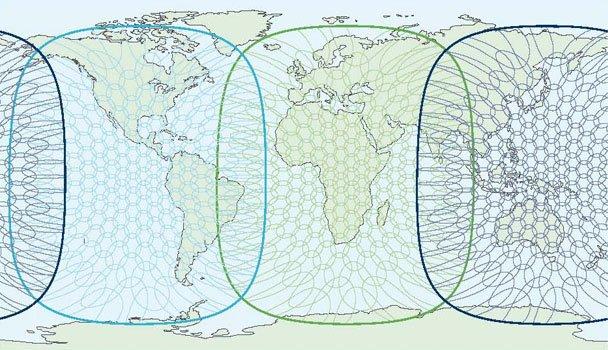
Spot (Narrow)-Beams for Seamless Coverage
There are 228 Spot beams for each of the I-4 Inmarsat/Viasat satellites.
Do you need any help?
If you have any questions about coverage, devices and airtime, please call or email us, or complete the form, and we'll be happy to help.